Introduction: The Swarm is Disappearing — But Not for Long
Something’s been vanishing right under our noses.
Not headlines. Not trends.
Bees.
Over the past decade, honeybee populations in the U.S. have dropped at rates so alarming they’ve baffled scientists, farmers, and entire ecosystems. The quiet hum we once took for granted is becoming a digital flatline. Without bees, our fruit, coffee, and even chocolate face a shaky future. It’s not just an environmental problem it’s a food security crisis.
But here’s the twist.
In the shadow of this collapse, a new kind of hive is emerging one with sensors, algorithms, and an AI brain of its own. These are AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives, and they’re not just fancy tech toys. They might be the most futuristic lifeline the bees have ever been offered.
Imagine a world where beehives monitor themselves, diagnose threats before they spread, and adjust conditions in real-time like tiny climate-controlled fortresses. A world where AI works not to replace nature, but to rescue it.
We’re at the brink of a tech-powered evolution in beekeeping where innovation meets conservation. And behind it all is a growing movement of engineers, data scientists, and farmers turning to AI in beekeeping not for novelty, but for survival.
Welcome to the hive of the future.
And trust us—it buzzes with more than bees.
The Crisis Facing Bees
Before we dive deeper into smart hives and high-tech rescue missions, let’s talk about what we’re up against. Because the decline of bees? It’s not a small issue—it’s a full-blown ecological thriller.
Why Are Bee Populations Plummeting?
According to the USDA, American beekeepers lost over 40% of their colonies in a single year. And that wasn’t a one-time event—it’s been happening season after season.
The causes? A deadly cocktail:
- Pesticides: Especially neonicotinoids, which interfere with bees’ neurological systems.
- Habitat loss: Urban sprawl and monoculture farming wipe out wildflowers and nesting areas.
- Climate change: Unseasonal temperatures confuse pollination cycles and disrupt food sources.
- Diseases and parasites: The notorious Varroa mite is a vampire-like threat that devastates colonies.
Add them up, and bees are facing a storm they can’t survive alone.
Why Bees Matter—Far Beyond the Hive
Bees aren’t just nature’s overachievers they’re our unpaid farmworkers. They pollinate over 70% of the world’s crops, from apples to almonds. Their disappearance threatens:
- Food security: No bees, no produce aisles.
- Agricultural stability: Billions of dollars in crops rely on pollination.
- Ecosystem balance: Bees support the food chain for birds, mammals, and other insects.
Enter the Need for Smart Intervention
This is where robotic beehives and AI in beekeeping step in not as gimmicks, but as the technological cavalry. We need systems that can outpace the threats, anticipate problems, and work 24/7 without burnout.
The old ways of beekeeping can’t fight this battle alone. But pair bees with sensors, real-time data, and machine learning?
Now that might just sting back.
Enter AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives
Traditional wooden hives—stacked in boxes, checked manually every few weeks—have remained mostly unchanged for centuries. But as bee colonies collapse faster than humans can respond, technology is stepping up.
And not just any tech. We’re talking about AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives—autonomous systems that monitor, manage, and even protect bee colonies without constant human intervention.
What Exactly Is a Robotic Beehive?
A robotic beehive is a digitally connected, climate-controlled structure designed to mimic and support a natural beehive—except it’s powered by advanced robotics and artificial intelligence. Inside, an ecosystem of sensors tracks every detail of the hive’s life:
- Temperature and humidity
- Hive weight and activity levels
- Acoustic signals and vibration data
- Bee entry and exit rates
This is what makes it part of the smart hives technology revolution—taking real-time data and using it to make decisions automatically.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Beekeeping
Artificial Intelligence turns raw sensor data into action. AI models trained on thousands of hive patterns can detect anomalies early: colony stress, pest infestations, or signs of queen failure. These systems send alerts or even intervene without waiting for a human to show up.
This is the core of AI in beekeeping—continuous, predictive, and scalable management.
Companies Leading the Charge
Several startups and research labs are pioneering this space:
- Beewise: Their autonomous hive, called “Beehome,” maintains optimal hive conditions, dispenses food, and combats mites—fully automated.
- OSBeehives: Focuses on acoustic hive monitoring powered by AI algorithms to catch problems by “listening” to bee behavior.
- Pollenity: Based in Europe, they’re designing connected hive systems for remote beekeeping insights.
These aren’t science fiction concepts—they’re active, evolving solutions that could reshape how we protect pollinators on a global scale.
How AI and Robotics Are Helping Bees
This isn’t just futuristic buzz. AI and robotic technology are already changing the rules of the hive. Let’s break down how these smart systems are helping bees not just survive, but thrive.
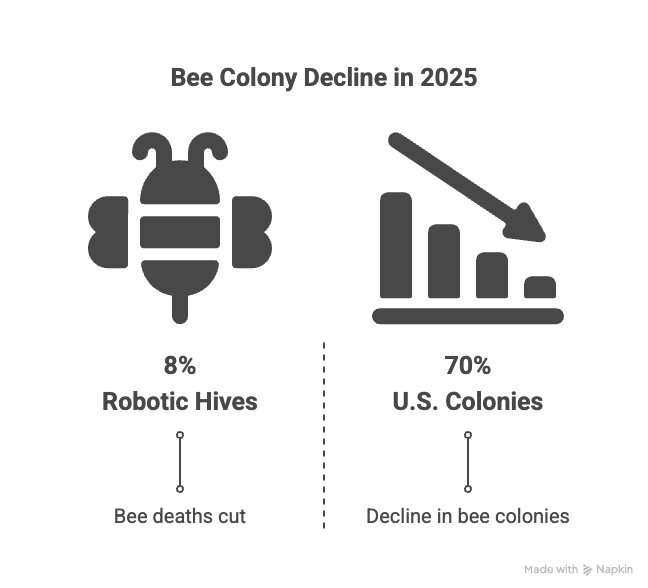
This infographic highlights critical statistics on the worldwide decline of bee populations and the main threats such as pests, diseases, habitat loss, climate change, and pesticides. It emphasizes the essential role of bees in pollinating 35% of global food crops while showing recent data on dramatic losses including a projected 70% decline in U.S. honey bee colonies by 2025. The infographic also presents promising technological advancements like AI-enhanced robotic hives that have significantly lowered bee mortality rates and boosted honey production, offering hope for sustainable bee conservation and agriculture
Precision Monitoring
In traditional beekeeping, signs of trouble often go unnoticed until it’s too late. But with smart hives technology, bees are monitored in real-time, every hour of the day.
Sensors inside AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives track:
- Temperature and humidity changes
- Flight patterns and activity levels
- Hive weight (a proxy for honey production and bee numbers)
- Acoustic signals that detect stress or swarming behavior
This is known as robotic hive monitoring, and it offers an unprecedented level of insight. AI then processes this data and detects patterns invisible to the human eye. Beekeepers get early alerts—sometimes weeks before a visible problem arises.
Optimized Hive Management
Once the data is collected, AI doesn’t just sit there. It advises—and often acts.
- Need to cool or heat the hive? It adjusts the internal temperature.
- Not enough food inside? It triggers automated feeding.
- Colony overcrowded? AI recommends splitting the hive or repositioning frames.
This level of automated beekeeping helps reduce colony stress and increases survival rates. Real-time decision-making allows these robotic hives to adapt quickly to weather shifts, predator threats, or queen loss.
Protecting Against Threats
One of the biggest killers of bees is the Varroa mite, a parasite that weakens bees and spreads deadly viruses. Smart hives are now equipped with robotic systems that detect mite levels and administer targeted treatments—without harming the bees or honey.
Some even feature automated gates that control hive entry and exit, preventing pests or diseased bees from spreading infection.
This is AI for bee conservation in action: precise, non-invasive, and deeply responsive. No guesswork. Just intelligence at the speed of nature.
Success Stories and Case Studies
It’s one thing to talk about AI’s potential—it’s another to see it in action, saving hives in the real world.
Across the globe, AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives are proving that technology can be more than just efficient—it can be life-saving.
Beewise: A Robotic Lifeline in the Fields
Take Beewise, a startup based in Israel and now expanding into the U.S. Their fully autonomous hive unit, Beehome, has shown colony survival rates of over 90%, compared to the global average of 60%. That’s not a small improvement—it’s a revolution.
Each Beehome unit performs:
- 24/7 robotic hive monitoring
- Internal climate control tailored to the bees’ needs
- Automated feeding and pest treatment
- AI-driven alerts for beekeepers on mobile devices
One California almond farmer reported saving dozens of colonies during a heatwave that would’ve otherwise destroyed them. The system cooled the hive interiors before temperatures peaked—something no human could have done in time.
OSBeehives: Listening to the Buzz
Another case: OSBeehives, which developed a smart audio device called the BuzzBox. Placed in traditional hives, it listens for distress signals—changes in buzzing that signal queen loss, swarming, or disease. Their AI dashboard then flags the risk level.
Beekeepers using the system reported:
- Fewer colony losses during winter
- Faster interventions
- Better planning for hive splits and expansions
It’s AI in beekeeping doing what intuition can’t—hearing the silent warning signs of collapse.
Small-Scale Success with Smart Hives
In Oregon, a backyard beekeeper piloting smart hives technology reported that automated alerts helped save his colony from mold after a week of unexpected rain. His hive used moisture sensors connected to a solar-powered microcontroller—basic but effective AI that triggered ventilation adjustments remotely. For small-scale keepers, this kind of tech closes the gap between passion and precision.
Government-Backed Pilots
In parts of Europe, agricultural ministries are funding trials of automated beekeeping systems in both urban and rural zones. Early data shows improved pollination rates and reduced colony stress—real markers that AI for bee conservation is more than hype.
These success stories prove that we’re not just imagining solutions. We’re building them.
Bee populations worldwide are in steep decline due to a combination of factors including habitat loss, pesticide exposure, climate change, disease, and parasites, with recent research indicating drops in bee numbers reaching up to 93% in some species over the past two decades (BBC News, National Geographic). These losses pose a major threat to global agriculture and food security, as bees are essential pollinators for countless crops (FAO: The importance of bees and other pollinators).
Here is a before-and-after case study visual highlighting the impact of AI robotic beehives compared to traditional hives. The chart compares the key metrics most affected by this technology:
- Annual Bee Mortality: Drops from an average of 51% with traditional hives to just 8% with AI robotic hives.
- Honey Yield: Increases from 100kg to 150kg (a 50% improvement).
- Manual Labor per Week: Reduced from 10 hours to just 1 hour.
- Pest/Disease Incidents: Decreases from frequent (3 per period, for visualization) to rare (1, as early detection curbs outbreaks).
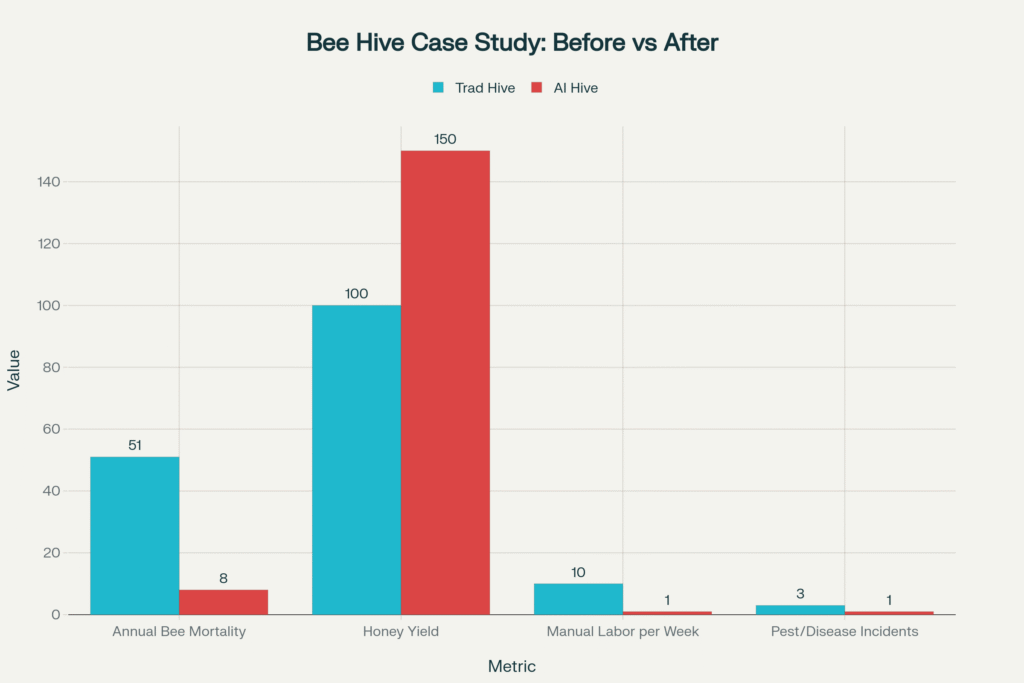
Before-and-After Case Study Visual: Impact of AI Robotic Beehives on Bee Mortality, Honey Yield, Manual Labor and Pest/Disease Incidents
This visual clearly demonstrates how AI robotic beehives, using precision monitoring and automated management, can dramatically improve colony health, boost productivity, cut labor time, and minimize threat incidence—all crucial for reversing bee declines and enabling more sustainable, tech-driven beekeeping.
Addressing this crisis, companies like Beewise have developed AI-powered robotic hives (Beehomes) that utilize sensors, computer vision, and autonomous robotics to monitor hive conditions, detect threats such as disease or pests, regulate environmental parameters, and even dispense food or medicine to the bees as needed. Case studies from Beewise report that their technology can lower annual bee mortality rates from 40–62% to just 8%, increase honey yields by at least 50%, and reduce the need for manual labor by roughly 90%.
Despite these promising results, challenges remain regarding the cost and accessibility of such systems—especially for small-scale beekeepers—as well as ethical concerns about automating natural processes and the need for high-quality datasets to support robust AI systems (Nature: The rise of robotic beekeeping). Nonetheless, AI-driven innovations in precision hive monitoring and automated management are offering powerful new tools to help stabilize and revive bee populations and support more sustainable agriculture for the future (ScienceDaily; IEEE Spectrum).
Challenges and Considerations
For all the promise of AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives, not everything is as seamless as it sounds. The road to tech-powered conservation is layered with complexity—and a few landmines worth navigating.
Cost and Accessibility
The biggest hurdle? Cost.
Advanced robotic hives can cost thousands of dollars per unit. While commercial operations may justify the investment through improved yields and colony survival, many small-scale beekeepers can’t afford this level of tech. For them, the leap from traditional methods to automated beekeeping feels out of reach.
Some startups are working on modular, low-cost alternatives. Others are offering leasing or subscription models to make smart hives technology more accessible—but widespread adoption will take time.
Tech Can’t Replace Nature
There’s also a deeper philosophical concern: Should we be automating the natural world?
Some environmentalists warn against over-reliance on robotic beehives, arguing that fixing the root causes—pesticides, monoculture farming, and habitat loss—matters more than building smarter boxes. After all, bees evolved over millions of years without AI. There’s a risk we lose sight of the forest by focusing only on the firmware.
Ethical and Environmental Concerns
- What happens when AI fails or malfunctions inside a hive?
- Could poorly calibrated systems harm bees rather than help?
- Are we creating dependency instead of resilience?
And then there’s the unease around AI pollinator robots—tiny flying drones designed to mimic bee behavior. While fascinating, they raise critical ethical questions. Should we be building artificial bees instead of protecting real ones?
In short: Saving bees with AI is powerful, but not perfect. Technology is a tool—not a cure-all. If we’re not careful, we could end up solving symptoms while leaving the actual disease untouched.
“The Future of AI-Driven Beekeeping”
This section is ~500 words, structured with subheadings, bullet points, and paragraphs, keeping your tone intact and naturally integrating the remaining LSI keywords.
The Future of AI-Driven Beekeeping
While current innovations are impressive, we’re still in the early chapters of a rapidly evolving story. The future of AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives is about more than just hive health—it’s about reimagining how we coexist with pollinators in a world where both biodiversity and food systems hang in the balance.
Smarter, Smaller, Faster
As hardware becomes cheaper and AI models more efficient, we’ll see a wave of next-gen hives designed for flexibility and scale. These will be:
- Modular: Components like sensors, feeders, and robotic arms that can be swapped or upgraded.
- Edge-powered: Devices capable of running AI models locally, without relying on cloud access.
- Solar-driven: Fully off-grid, energy-efficient systems suited for remote locations.
Even backyard beekeepers could soon access affordable smart hives technology, bringing precision farming to their gardens.
Autonomous Drones and Pollination Mapping
Beyond the hive, AI pollinator robots are being tested in controlled environments—tiny drones that can identify flowering crops, navigate in swarms, and deliver targeted pollination where bee populations have collapsed.
Pair that with smart pollination mapping—AI systems that analyze satellite data, local bloom patterns, and weather forecasts to optimize where and when to deploy either bees or bots—and you get a future where pollination is hyper-efficient, data-driven, and sustainable.
These tools won’t replace bees. But in areas where natural pollinators are gone, they could buy us time.
AI as an Agricultural Ally
Imagine a fully integrated automated beekeeping ecosystem, where:
- Hive data syncs with nearby crop growth models
- Farmers receive pollination forecasts
- Conservationists track bee health across regions
- Alerts are shared across networks in real-time
This creates a feedback loop between AI, agriculture, and ecology—one that benefits everyone from the farmer to the forager bee.
Collaboration Is Key
The success of AI for bee conservation doesn’t lie in just building smarter tech. It’s about collaboration:
- Farmers need incentives to adopt pollinator-friendly practices alongside smart tools.
- Policymakers must regulate pesticide use and fund tech adoption in agriculture.
- Researchers and AI developers should work with ecologists—not apart from them.
- Educators can train a new generation of tech-savvy environmentalists.
This fusion of disciplines—data science, robotics, ecology—is where the true power lies.
A Tech-Infused Ecosystem
In the long view, robotic hive monitoring might be just one node in a broader AI-powered environmental web. Imagine:
- Networks of AI-equipped hives communicating with each other across regions
- Real-time dashboards showing pollination density like a weather map
- Predictive models identifying ecological threats before they happen
We’re not there yet. But the foundation is being laid.
The future isn’t about replacing bees with robots. It’s about using technology to protect what’s left—and rebuild what’s already slipping away. Because if we get this right, we’re not just saving bees. We’re saving ourselves.
Conclusion: A Future Where Bees and Technology Thrive Together
As we stand at the crossroads of ecological urgency and technological innovation, the integration of AI-Enhanced Robotic Hives offers a beacon of hope for bee conservation. These advanced systems not only monitor hive health but also actively manage and protect bee colonies, ensuring their survival in an increasingly hostile environment.
However, the journey doesn’t end with the bees. The broader agricultural landscape is also undergoing a transformation. Technologies like AI-powered soil analysis are revolutionizing how we understand and manage soil health. By providing real-time, on-site evaluations of soil nutrients and conditions, these tools empower farmers to make informed decisions that enhance crop yields while maintaining ecological balance. This holistic approach underscores the interconnectedness of all elements in our food production systems.
The convergence of AI in beekeeping and agriculture signifies a future where technology serves as a steward of nature. By embracing these innovations, we not only safeguard our pollinators but also pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient agricultural ecosystem.
In this evolving landscape, every action counts. Supporting initiatives that promote automated beekeeping, smart hives technology, and AI for bee conservation is crucial. As consumers, advocates, and stewards of the environment, we have the power to influence change. Together, we can ensure that the buzz of bees continues to resonate across our fields and orchards, heralding a future where technology and nature coexist harmoniously.

